桥接模式在JDBC源码中的应用
在 JDBC API 中,大家非常熟悉的 Driver 类就是桥接对象。使用 JDBC 时通过 Class.forName() 方法可以动态加载各个数据库厂商实现的 Driver 类。
下面以 MySQL 的实现为例,具体客户端应用代码如下:
当我们执行到 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") 方法的时候,就会执行 com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 类的静态块中的代码。静态块中的代码只是调用了一下 DriverManager 的 registerDriver() 方法,然后将 Driver 对象注册到 DriverManager 中。下面继续跟进 DriverManager 类,相关代码如下。
下面以 MySQL 的实现为例,具体客户端应用代码如下:
// 1. 注册JDBC驱动
// 反射机制加载驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获取连接Connection
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL,USER,PASS);
// 3. 获取sql语句的对象Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 4. 执行sql语句,并返回结果
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
以下为 Driver 接口的定义。
public interface Driver {
Connection connect(String url, java.util.Properties info) throws SQLException;
boolean acceptsURL(String url) throws SQLException;
DriverPropertyInfo[] getPropertyInfo(String url, java.util.Properties info) throws SQLException;
int getMajorVersion();
int getMinorVersion();
boolean jdbcCompliant();
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
}
Driver 在 JDBC 中并没有具体实现,具体的功能实现由各厂商完成,下面是 MySQL 中 Driver 的具体实现。
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
Driver 实现类的代码特别简短,其中只调用了 DriverManager 中的 registerDriver 方法来注册驱动。当驱动注册完成后,就会开始调用 DriverManager 中的 getConnection 方法了。当我们执行到 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") 方法的时候,就会执行 com.mysql.jdbc.Driver 类的静态块中的代码。静态块中的代码只是调用了一下 DriverManager 的 registerDriver() 方法,然后将 Driver 对象注册到 DriverManager 中。下面继续跟进 DriverManager 类,相关代码如下。
public class DriverManager {
// List of registered JDBC drivers
private final static CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo> registeredDrivers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo>();
private static volatile int loginTimeout = 0;
......
private final static Object logSync = new Object();
private DriverManager(){}
static {
loadInitialDrivers();
println("JDBC DriverManager initialized");
}
......
public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver)
throws SQLException {
if(driver != null) {
registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver));
} else {
// This is for compatibility with the original DriverManager
throw new NullPointerException();
}
println("registerDriver: " + driver);
}
......
}
在注册之前,将传过来的 Driver 对象封装成一个 DriverInfo 对象。
class DriverInfo {
final Driver driver;
DriverInfo(Driver driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public boolean equals(Object other) {
return (other instanceof DriverInfo)
&& this.driver == ((DriverInfo) other).driver;
}
public int hashCode() {
return driver.hashCode();
}
public String toString() {
return ("driver[className=" + driver + "]");
}
}
DriverInfo 本身其实就是 Driver。接下来继续执行客户端代码的第二步,调用 DriverManager 的 getConnection() 方法获取连接对象,下面跟进源码。
public class DriverManager{
......
public static Connection getConnection(String url,
java.util.Properties info) throws SQLException {
return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));
}
public static Connection getConnection(String url,
String user, String password) throws SQLException {
java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties();
if (user != null) {
info.put("user", user);
}
if (password != null) {
info.put("password", password);
}
return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));
}
public static Connection getConnection(String url)
throws SQLException {
java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties();
return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));
}
private static Connection getConnection(
String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException {
ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;
synchronized (DriverManager.class) {
// synchronize loading of the correct classloader.
if (callerCL == null) {
callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
}
if(url == null) {
throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");
}
println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");
SQLException reason = null;
for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
try {
println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
if (con != null) {
// Success!
println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
return (con);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
if (reason != null) {
println("getConnection failed: " + reason);
throw reason;
}
println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url);
throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001");
}
}
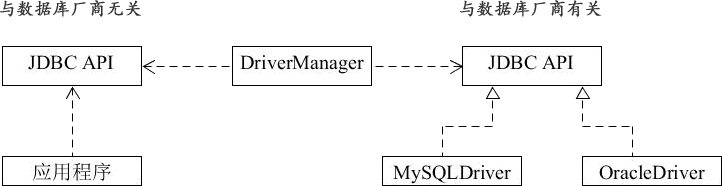
在 getConnection() 中,又会调用各自厂商实现的 Driver 的 connect() 方法获得连接对象。这样就巧妙地避开了使用继承,为不同的数据库提供了相同的接口。JDBC API 中的 DriverManager 就是桥,如下图所示。
所有教程
- C语言入门
- C语言编译器
- C语言项目案例
- 数据结构
- C++
- STL
- C++11
- socket
- GCC
- GDB
- Makefile
- OpenCV
- Qt教程
- Unity 3D
- UE4
- 游戏引擎
- Python
- Python并发编程
- TensorFlow
- Django
- NumPy
- Linux
- Shell
- Java教程
- 设计模式
- Java Swing
- Servlet
- JSP教程
- Struts2
- Maven
- Spring
- Spring MVC
- Spring Boot
- Spring Cloud
- Hibernate
- Mybatis
- MySQL教程
- MySQL函数
- NoSQL
- Redis
- MongoDB
- HBase
- Go语言
- C#
- MATLAB
- JavaScript
- Bootstrap
- HTML
- CSS教程
- PHP
- 汇编语言
- TCP/IP
- vi命令
- Android教程
- 区块链
- Docker
- 大数据
- 云计算