模板方法模式在MyBatis源码中的应用
在 MyBatis 源码中,有很多模板方法模式的经典应用场景。
本节来介绍模板方法模式在 BaseExecutor 类中的应用。BaseExecutor 是一个基础的 SQL 执行类,实现了大部分 SQL 执行逻辑,然后把几个方法交给子类定制化完成,主要提供了缓存管理和事务管理的基本功能。源码如下。
doUpdate、doFlushStatements、doQuery 和 doQueryCursor 这几个方法就是交由子类来实现的,也就是说继承 BaseExecutor 的子类只需要实现这 4 个基本方法来完成数据库的相关操作即可。
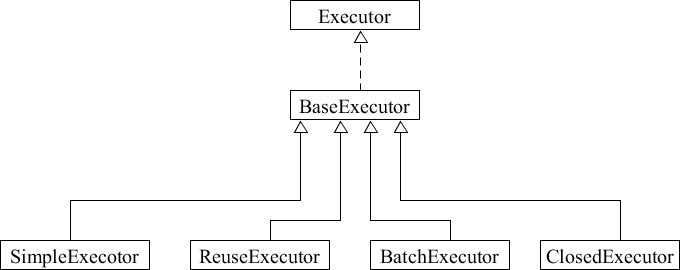
BaseExecutor 的子类有 ReuseExecutor、SimpleExecutor、BatchExecutor 和 ClosedExecutor,其类图如下。
这里对这 4 个子类的功能简单介绍一下:
下面是 SimpleExecutor 的 doUpdate() 方法实现。
本节来介绍模板方法模式在 BaseExecutor 类中的应用。BaseExecutor 是一个基础的 SQL 执行类,实现了大部分 SQL 执行逻辑,然后把几个方法交给子类定制化完成,主要提供了缓存管理和事务管理的基本功能。源码如下。
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
protected Transaction transaction;
protected Executor wrapper;
protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad> deferredLoads;
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;
protected Configuration configuration;
protected int queryStack = 0;
private boolean closed;
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
// 省略....
Executor 是 Mybatis 的核心接口之一,定义了数据库操作的基本方法。BaseExecutor 类中的 query() 方法会先创建 CacheKey 对象,并根据 CacheKey 对象查找一级缓存,如果缓存命中则返回缓存中记录的结果对象,如果未命中则查询数据库得到结果集,之后将结果集映射成结果对象并保存到一级缓存中,同时返回结果对象。doUpdate、doFlushStatements、doQuery 和 doQueryCursor 这几个方法就是交由子类来实现的,也就是说继承 BaseExecutor 的子类只需要实现这 4 个基本方法来完成数据库的相关操作即可。
BaseExecutor 的子类有 ReuseExecutor、SimpleExecutor、BatchExecutor 和 ClosedExecutor,其类图如下。

这里对这 4 个子类的功能简单介绍一下:
- SimpleExecutor 是 Mybatis 执行 Mapper 语句时默认使用的 Executor,提供最基本的 Mapper 语句执行功能,没有过多的封装。
- ReuseExecutor 提供了 Statement 重用的功能,通过 statementMap 字段缓存使用过的 Statement 对象进行重用,可以减少 SQL 预编译以及创建和销毁 Statement 对象的开销,从而提高性能。
- BatchExecutor 实现了批处理多条 SQL 语句的功能,在客户端缓存多条 SQL 并在合适的时机将多条 SQL 打包发送给数据库执行,从而减少网络方面的开销,提升系统的性能。
- ClosedExecutor 只是某个类的一个内部类。
下面是 SimpleExecutor 的 doUpdate() 方法实现。
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
int var6;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, (ResultHandler)null, (BoundSql)null);
stmt = this.prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
var6 = handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
this.closeStatement(stmt);
}
return var6;
}
再来对比一下 BatchExecutor 的 doUpdate() 方法实现。
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameterObject, RowBounds.DEFAULT, (ResultHandler)null, (BoundSql)null);
BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
Statement stmt;
if (sql.equals(this.currentSql) && ms.equals(this.currentStatement)) {
int last = this.statementList.size() - 1;
stmt = (Statement)this.statementList.get(last);
handler.parameterize(stmt);
BatchResult batchResult = (BatchResult)this.batchResultList.get(last);
batchResult.addParameterObject(parameterObject);
} else {
Connection connection = this.getConnection(ms.getStatementLog());
stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
handler.parameterize(stmt);
this.currentSql = sql;
this.currentStatement = ms;
this.statementList.add(stmt);
this.batchResultList.add(new BatchResult(ms, sql, parameterObject));
}
handler.batch(stmt);
return -2147482646;
}
细心的小伙伴一定看出了差异,BatchExecutor 的处理逻辑比 SimpleExecutor 更为复杂,调用的核心 API 也有区别,SimpleExecutor 调用的核心方法是 handler.update() 方法,BatchExecutor 调用的核心方法是 handler.batch() 方法。这里暂时不对 MyBatis 源码进行深入分析,感兴趣的小伙伴可以自行继续深入研究。所有教程
- C语言入门
- C语言编译器
- C语言项目案例
- 数据结构
- C++
- STL
- C++11
- socket
- GCC
- GDB
- Makefile
- OpenCV
- Qt教程
- Unity 3D
- UE4
- 游戏引擎
- Python
- Python并发编程
- TensorFlow
- Django
- NumPy
- Linux
- Shell
- Java教程
- 设计模式
- Java Swing
- Servlet
- JSP教程
- Struts2
- Maven
- Spring
- Spring MVC
- Spring Boot
- Spring Cloud
- Hibernate
- Mybatis
- MySQL教程
- MySQL函数
- NoSQL
- Redis
- MongoDB
- HBase
- Go语言
- C#
- MATLAB
- JavaScript
- Bootstrap
- HTML
- CSS教程
- PHP
- 汇编语言
- TCP/IP
- vi命令
- Android教程
- 区块链
- Docker
- 大数据
- 云计算